4MOST Media: Photo and Video Documentation
Welcome to the media page of the 4MOST project at the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP). Here you will find a comprehensive collection of photos and videos documenting the development, integration, and preparation of 4MOST – one of Europe’s largest ground-based astronomical instruments.
These materials are available for editorial use. Please credit the AIP or the indicated source when publishing. For additional media content or inquiries, feel free to contact presse@aip.de.
- Images:
- Videos
- General Information about 4MOST (press releases, YouTube talks, website)
First Light: First observations in October 2025

Sky region of the first observations with 4MOST with an example spectrum. In the Sculptor Galaxy (top right), 4MOST took spectra from its centre, star-forming regions and globular clusters. The old stars of the globular cluster NGC 288 (bottom left) from the outskirts of our Milky Way showed hardly any signatures of heavy elements. The coloured line in the image corresponds to spectrum captured with 4MOST of a distant galaxy with an active nucleus.
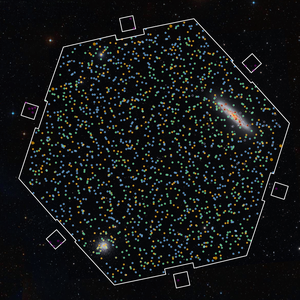
The "First Light" field of view with targets of the 4MOST fibres shown as coloured circles (orange: galactic centre of the Sculptor Galaxy, red: planetary nebula, dark blue: star cluster in the Sculptor Galaxy, yellow: bright Gaia stars, light blue: faint Gaia stars, green: galaxies (in the background), purple (in the squares around the field): guide stars; the ring colour indicates high-resolution (orange) or low-resolution spectrograph (light blue)).
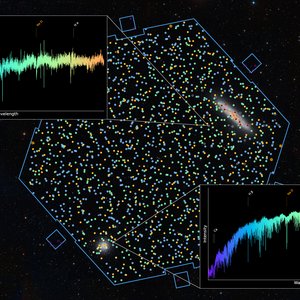
The sky around the Sculptor Galaxy NGC 253 and the globular cluster NGC 288 was the target of the first observations with 4MOST. The blue frame shows the boundary of 4MOST's field of view. Each circle symbolises one of the more than 2400 fibres. The embedded images show the spectrum of a stellar cluster in the Sculptor galaxy (top) and the spectrum of a star in the globular cluster (bottom).
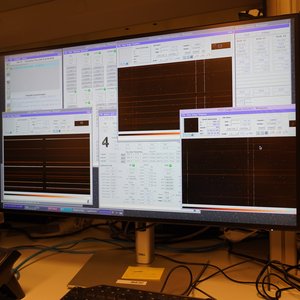
The first observation data are being taken. In the control room everything is supervised.

People in the control room of the telescope are looking at the first data.

The people from the team that were on-site in Chile are happy about the first successful observations.
September 2025: Installation of the final components in Chile

One of the three 4MOST spectrographs is on its way from the ground station to the mountain.

The crane carefully lifts the sensitive equipment into the air.

Ropes are used to steer the spectrograph in the right direction.

The spectrograph has arrived safely in the dome.

The optical fibre-slit is being installed at one of the low-resolution spectrographs.

The low-resolution spectrographs still need to be connected to the telescope.

Both low-resolution spectrographs were installed successfully at the VISTA telescope in September 2025.

The high-resolution spectrograph - the final component (!) - is being prepared for transport at the ground base.

The high-resolution spectrograph on its way to the VISTA telescope.

The crane lifts the spectrograph through the dome opening.

The third spectrograph is now also fixed at its final position at the telescope.

The glass fibres still need to be connected with the spectrographs.

The glass fibres conduct the light from the telescope to the spectrographs.

The hardware components of 4MOST are fully installed on the VISTA telescope. The telescope is ready to capture its first starlight!
At AIP in May 2025
At AIP in Potsdam in May 2025, the last components were being prepared for transportation to Chile. Parts of the AESOP fiber positioner, the fiber system and the high-resolution spectrograph could then still be seen in the Leibnizhaus integration hall.

The Leibnizhaus, where the final components of 4MOST were still visible in the integration hall.

The Fibre Positioner System (AESOP) is a robotic system that simultaneously positions 2436 glass fibres to catch the light of stars and galaxies and transfer it to the spectrographs.
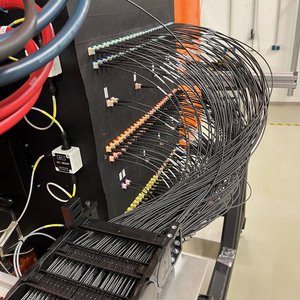
The fibre system transports light from the telescope to the spectrographs through glass fibres of 85 micron diameter, about the diameter of a human hair. The picture shows about 200 black, plastic conduits that hold 10–15 fibres each ending in the colourful connectors at the back of the AESOP positioner system.

The High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) breaks the light of 812 objects in its colours with high precision and detail. This allows accurate velocity measurements and provides detailed information on chemical element abundances in the target objects.
Paranal in Chile and VISTA Telescope - Home of 4MOST
The 4MOST instrument is installed at the VISTA telescope, which belongs to ESO'S Paranal Observatorium in the Chilenian Atacama Desert.

The Milky Way just before sunrise at Cerro Paranal, Chile.

Evening at Paranal

Sunset at Parnanal

The hilly landscape at Paranal. On the large hill you can just see the Very Large Telescope with its 4 domes. The VISTA telescope is on to the right on the smaller hill.

The VISTA telescope from afar

The Paranal Observatory is located in the Atacama desert in Chile.

The VISTA telescope (left), in the background the Very Large Telescope (4 domes, right). The Milky Way and the Magellanic Clouds are visible in the sky.

The VISTA telescope building at sunset

The VISTA telescope with open dome slit

The VISTA telescope with open dome slit at night

During the installation at the VISTA telescope

View from above at the VISTA telescope

View from above to the front of the VISTA telescope, with a view into the hall below, from where the 4MOST components are brought to the telescope by crane.

The VISTA telescope with Cassegrain Cable Wrap unit

The VISTA telescope with Cassegrain Cable Wrap unit. At the left you can still see the stand of the unit (orange).

Preparations at the VISTA telescope 2019
Installation of 4MOST at the VISTA telescope in Chile
Since 2024, first components of 4MOST have been installed and tested at the VISTA telescope.

A forklift truck brings the crates containing the 4MOST components to the ground floor of the VISTA telescope building.

Forklift truck with one of the 4MOST crates on its way to the VISTA telescope building.

The Cassegrain Cable Wrap (CaCW) prevents twisting or tearing of cables and opitcal fibres during rotation of the telescope.

The Cassegrain Cable Wrap is being installed at the VISTA telescope

Installation of 4MOST components at the VISTA telescope

Installation of 4MOST components at the VISTA telescope

The VISTA telescope. The Cassegrain Cable Wrap and the AESOP fibre positioner, which aligns the 2436 individual glass fibres very precisely to the desired celestial objects, are already installed.

The VISTA telescope with open dome

The Focal Surface Test Tool just before installation

The Focal Surface Test Tool is being brought to the telescope via crane.

The Focal Surface Test Tool next to the VISTA telescope

The "Aquisition, Guiding and Wavefront Sensor Unit" (AGW) keeps the telescope pointed on targets and optics in correct shape during observations.

The AWG unit is being installed.

The Wide Field Corrector, a system of lenses with 65 to 90 cm diameter, for correcting optical abberations

The Wide Field Corrector in its stand before installation

The Wide Field Corrector directly above the ground opening through which it was lifted to the telescope

The wide field corrector ‘floats’ to the telescope.

Installation of the Wide Field Corrector

The Wide-Field Corrector is brought to the telescope via crane.

Wide-angle image of the WFC in front of the VISTA telescope

The Wide Field Corrector is carefully being integrated into the telescope.

View into the lenses of the Wide Field Corrector

Installation of 4MOST components at the VISTA telescope

Some members of the 4MOST installation team. Many employees from various scientific and technical departments of the AIP were on site to carry out the installation and tests.

The 4MOST team in front of the VISTA telescope building
Transport preparations in Potsdam
The ‘Cassegrain Cable Wrap’ unit was the first large 4MOST component to be sent on its way to Chile in February 2024 after extensive testing in Potsdam.
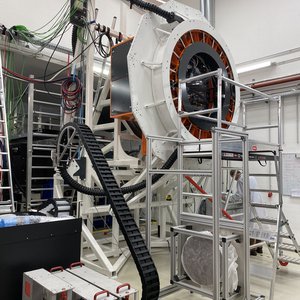
The Cassegrain Cable Wrap in AIP's integration hall in Potsdam in July 2023.

The Cassegrain Cable Wrap is preparement for its shipment to Chile.

Everything is neatly sorted and packed for transport.

The stand of the Cable Wrap also needs to be packed and shipped.

A 4MOST component often requires several crates, which are shipped to Chile by land, air and/or sea.

The 4MOST Cable Wrap System during its packaging in preparation for shipping.

Loading a container with 4MOST components onto a lorry in front of the AIP's Schwarzschildhaus, where one of the AIP's integration halls is located.

The lorry has already loaded both containers and will start its journey.

May 2025: The last, smaller componts for 4MOST are packed into transport boxes.

Carefully packed, the last load will soon start its journey to Chile.

The boxes in front of the Schwarzschildhaus which houses one of the AIP's integration halls.
Integration and testing at AIP in Potsdam
The AIP is equipped with two integration halls. There, technicians, engineers and scientists can thoroughly examine various observation instruments and their individual components and test their interaction with each other.

In the AIP integration hall in the Leibnizhaus

The telescope stand, back view. The 4MOST components are installed at this stand for testing their functionality.

The AESOP fibre positioner arrived from Australia in October 2023 in Potsdam. Overview of the boxes with the individual components.

The team that accompanied the unpacking of the AESOP components.

Brief discussion when unpacking the 4MOST components

Each box must be openend carefully and checked for its content.

During unboxing of the 4MOST components
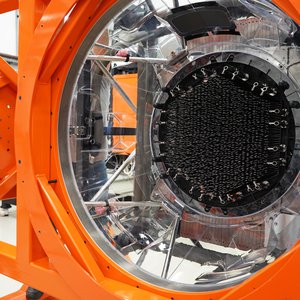
AESOP is used to align the 2436 glass fibres precisely to the desired celestial objects so that their light can be analysed.

Assembly of one of the 4MOST spectrographs in the Leibnizhaus integration hall of the AIP

The lens is being moved by crane to the correct position.

The spectrographs for 4MOST will split the light of stars and galaxies into its colour components.

Specialists and careful teamwork are required to assemble the individual components.

Looking through the new Wide Field Corrector of the 4MOST instrument. The special coatings on the 65-to-90-centimetre diameter lenses in the corrector cause colourful reflections of the bright fluorescence lights on the ceiling of the integration hall at AIP.
Videos
General Information about 4MOST
News about 4MOST at the AIP website
- May 2025: Final destination Chile: 4MOST leaves Europe – Last Look Behind the Scenes
- February 2024: 4MOST milestone: first major shipment to Chile
- April 2022: 4MOST spectograph sees first light in Potsdam
- October 2021: Starlight catching system for 4MOST is unpacked in Potsdam
- March 2019: Milky Way and beyond: Next Generation Survey Telescope
- August 2016: ESO and AIP sign agreement to build 4MOST
Talk about 4MOST on YouTube
- Zukunft der Astronomie • Entschlüsselung des Universums mit 4MOST | Joar Brynnel, Andreas Kelz (German)
- Exploring the Universe & the Future of Sky Observation • 4MOST | Roelof de Jong (English)
4MOST project website
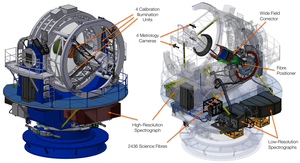
Overview of the components of the 4MOST instrument
Credit: 4MOST Consortium
